Basic Concepts: Difference between revisions
From Jedisaber Wiki
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=== CIA Triad === | === CIA Triad === | ||
[[File:Sec_objectives.jpg]] | [[File:Sec_objectives.jpg|600px|thumb|center]] | ||
The three key objectives (CIA Triad) of cybersecurity programs are confidentiality, integrity, and availability. | The three key objectives (CIA Triad) of cybersecurity programs are confidentiality, integrity, and availability. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
=== DAD Triad === | === DAD Triad === | ||
[[File:Sec_DAD.jpg|600px|thumb|center]] | |||
The the three key threats to cybersecurity efforts: disclosure, alteration, and denial. | |||
- Disclosure: exposure of sensitive information to unauthorized individuals; violation of the principle of confidentiality | |||
(Attacks on the system, misconfigured credentials, lost devices) | |||
- Alteration: unauthorized modification of information; violation of the principle of integrity | |||
(fraudulent transactions, typos, bit flip due to power loss) | |||
- Denial: disruption of an authorized user's legitimate access to information; violation of the principle of availability | |||
(DDoS, failure of a server) | |||
=== Practical Application === | |||
You can use the CIA and DAD models as a starting point for a more detailed risk analysis. | |||
Security incidents occur when there is a breach of the confidentiality, integrity, and/or availability of information or systems. | |||
CIA and DAD triads can be a useful staring point. | |||
For example, in assessing threats to your website, you can apply the DAD triad: | |||
- '''Disclosure:''' Does the site contain sensitive information that would damage the company if it was disclosed at an attacker? | |||
- '''Alteration:''' If an attacker was able to modify information contained on the site, would that cause financial, reputational, or operational damage? | |||
- '''Denial:''' Does the website perform mission-critical activities that could damage the business significantly if an attacker were able to disrupt the site? | |||
=== Impacts of a breech === | |||
A security incident can have several types of risk. | |||
Types of risk: | |||
- '''Financial Risk''' | |||
Monetary damage. Equipment and/or facilities may have to be repairs or replaced. | |||
Indirectly, plans or information may be lost that may cost money to re-create (or information could go to a competitor that | |||
- '''Reputational Risk''' | |||
Negative publicity about a security incident. (Can effect customers, employees, suppliers, and stakeholders opinions.) | |||
- '''Strategic Risk''' | |||
An organization may become less effective in meeting its major goals and objectives as a result of the breach. | |||
- '''Operational Risk''' | |||
Risk to the organization's ability to carry out its day-to-day functions. | |||
- '''Compliance Risk''' | |||
When a security breach causes an organization to run afoul of legal or regulatory requirements. | |||
(Example: HIPAA compliance failures, such as losing patient files.) | |||
'''Note:''' Risk can be in more than one category. | |||
Latest revision as of 19:21, 6 June 2025
CIA Triad
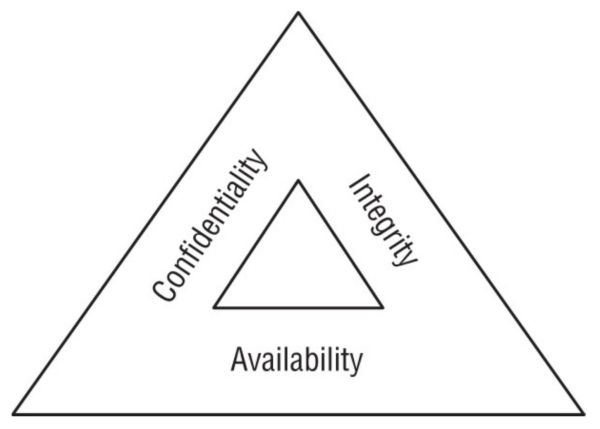
The three key objectives (CIA Triad) of cybersecurity programs are confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
- Confidentiality: Unauthorized users don't gain access. (Firewalls, ACL's, encryption)
- Integrity: No unauthorized modifications. (Hashing, monitoring)
- Availability: The system is up when users need it. (fault tolerance, clustering, backups)
Nonrepudiation: Someone who performed an action can't deny performing said action (Digital Signatures) (Not a part of CIA, but also important.)
DAD Triad
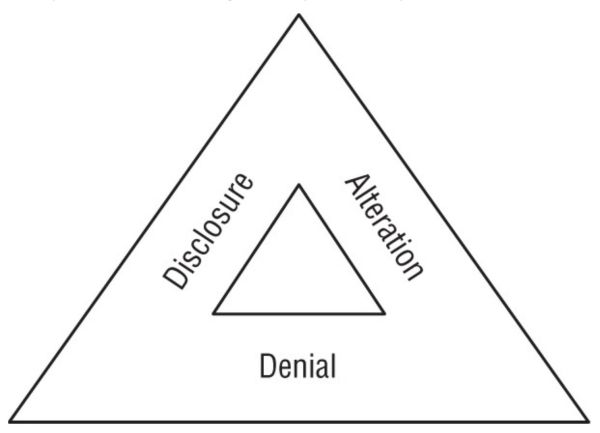
The the three key threats to cybersecurity efforts: disclosure, alteration, and denial.
- Disclosure: exposure of sensitive information to unauthorized individuals; violation of the principle of confidentiality (Attacks on the system, misconfigured credentials, lost devices)
- Alteration: unauthorized modification of information; violation of the principle of integrity (fraudulent transactions, typos, bit flip due to power loss)
- Denial: disruption of an authorized user's legitimate access to information; violation of the principle of availability (DDoS, failure of a server)
Practical Application
You can use the CIA and DAD models as a starting point for a more detailed risk analysis.
Security incidents occur when there is a breach of the confidentiality, integrity, and/or availability of information or systems.
CIA and DAD triads can be a useful staring point.
For example, in assessing threats to your website, you can apply the DAD triad:
- Disclosure: Does the site contain sensitive information that would damage the company if it was disclosed at an attacker?
- Alteration: If an attacker was able to modify information contained on the site, would that cause financial, reputational, or operational damage?
- Denial: Does the website perform mission-critical activities that could damage the business significantly if an attacker were able to disrupt the site?
Impacts of a breech
A security incident can have several types of risk.
Types of risk:
- Financial Risk
Monetary damage. Equipment and/or facilities may have to be repairs or replaced. Indirectly, plans or information may be lost that may cost money to re-create (or information could go to a competitor that
- Reputational Risk
Negative publicity about a security incident. (Can effect customers, employees, suppliers, and stakeholders opinions.)
- Strategic Risk
An organization may become less effective in meeting its major goals and objectives as a result of the breach.
- Operational Risk
Risk to the organization's ability to carry out its day-to-day functions.
- Compliance Risk
When a security breach causes an organization to run afoul of legal or regulatory requirements. (Example: HIPAA compliance failures, such as losing patient files.)
Note: Risk can be in more than one category.
